

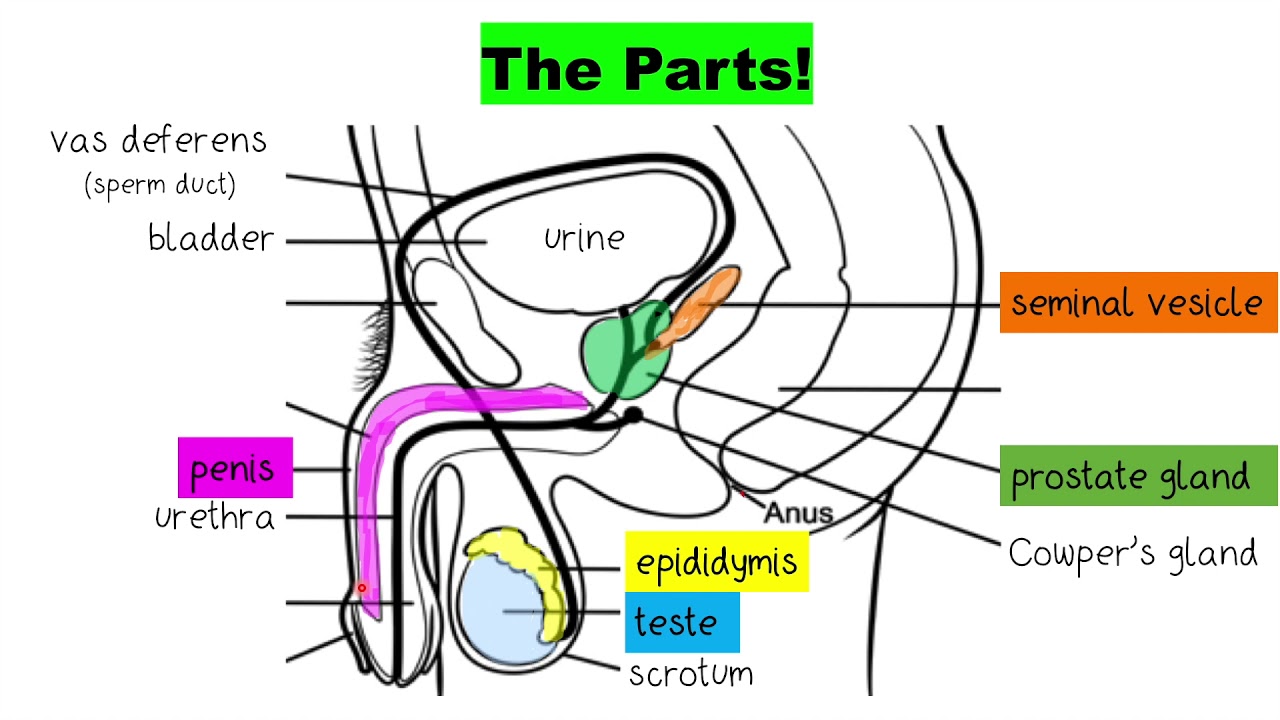
The seminal vesicles sit superiorly to the prostate, and drain a fructose-rich alkaline fluid into the prostatic urethra. In Q: Draw a well labelled diagram of female reproductive. They produce a mucus secretion which serves as lubrication, expels any urine residue from the urethra and neutralises residual acidity within the urethra. A: The male reproductive system is a organ system in males used for the process of reproduction. The bulbourethral glands, or Cowper’s glands, are located posterolaterally to the membranous urethra. The prostate’s anatomy consists of three zones, the central, transitional and peripheral zones, where different pathologies arise. These enzymes enter the prostatic urethra via the prostatic ducts. It secretes enzymes into the semen which maintain the semen’s fluid state. The prostate gland sits inferiorly to the bladder. Many important structures run in this bundle, including the testicular artery, pampiniform plexus of testicular veins and vas deferens. The spermatic cord is a collection of blood vessels, nerves and ducts that connect the testes to the pelvic cavity.
Semen with mature sperm is transported through this tube to the urethra for ejaculation. It travels through the pelvic cavity and right behind the urinary bladder. Vas Deferens It is a long and muscular tube that connects the epididymis to the urethra.
Diagrams of male reproductive system skin#
The dartos muscle is located deep to the skin and helps adjust the surface area of the scrotum, and therefore its internal temperature. The structure of male reproductive system organs present inside the body are: 1. The scrotum is a fibromuscular sac located posteriorly to the penis. This system consists of a pair of testes and a network of excretory ducts (epididymis, ductus deferens (vas deferens), and ejaculatory ducts), seminal vesicles. This is the location of sperm production, maturation and storage. The testes and epididymis are located in the scrotum, suspended by the spermatic cord. The penis has three main anatomical sections: the root (where the penis is fixed to the pelvic floor), the body (the length of the penis) and the glans (where the urethral opening is located). The male reproductive system can be split into seven parts: the penis, the testes and epididymis, the scrotum, the spermatic cord, the prostate gland, the bulbourethral glands and the seminal vesicles. Some tissues sit outside of the pelvis, in the scrotum, which provides a cooler environment. The male reproductive system mainly resides within the pelvis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
